Trp Ruen, ruenithic
from 567 “V les knig”
(In wooden books)
Unlike the old slavonic, the consonantal system of the ancient macedonian language is characterised with some of it’s own peculiarities in articulation. In that way for instance for the sonant
![]()
exists an appropriate separate sign which is identical with the one from the contemporary macedonian literal language and which is pronounced in two ways: as a strongly articulated consonant and as a less tensely spoken unsyllaboforming sound. Not even in one deciphered ancient macedonian text the presence of the small use or the big use has been registered or the big nasal, nor is the yor, yeri, yer, yat or KSI: the Ruenithic hasn’t registered the letters:
¿, ¿I, ì, î
but on the other hand Trp Ruen used the letters:
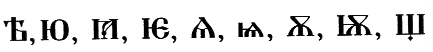
while cutting (writing) on the oldest
uptill now preserved middle aged history of the slav people with an absolute
chronology from around the year 650 up to, probably the year 567 (or the
IXth cent. A.D.) because on the ninth row of the facsimile of the little
plank number 15 of the oak planks with the length of 38 cm, width 22 cm
and thickness of 6 up to 10 mm on the so called “VLESOVA
KNIGA” “VLESOVA KNIGA” (“In Wood Book”),
that is “V LES KNIG”
“V LES KNIG”, that is:

“VO DRVENITE KNIGI” “VO DRVENITE KNIGI” (”In the wooden book”) it clearly and authentically is cut out (written):

and this appropriately translated in modern macedonian literal language sounds:
“RECKANO
E 6075 KAJ SNAATA COJA.
TRP RUEN - (U)CEN OD OVOJ DVOREC”
“RECKANO E 6075
KAJ SNAATA COJA.
TRP RUEN - (U)CHEN OD OVOJ DVOREC”
“IT IS COU OUT
(WRITTEN) 6075 AT THE DAUGHTER – IN – LAW’S TSOYA
TRP RUEN EDUCATED FROM THIS COURT”.
Even though we don’t have access and inspection to all the facsimiles of the “V LES KNIG” (“V LES KNIG”) and are aware of the mistakes that J.P. Miroljubov could make while blindly copying the unfamiliar content, which for him was written with an unknown alphabet and with an unknown language, even so, from the deciphered accessible facsimile on the wooden plank number 15 the notion importunes that both the letter alphabet and the language which Trp Ruen used are much closer to their ancient macedonian base then they are to the familiar middleage modifications of the reformers Kiril and Metodi and of Kliment Ohridski. Namely, Trp Ruen doesn’t use yor, yer and yeri doesn’t use the diagram “ ou”, instead only the ligature “$” and the ancient macedonian sign “u” for the vowel “ U” Judging by the wooden piece no. 15 of “V LES KNIG…” he most probably knew and used only a few individual signs for the diphthongs and nasal sounds (see comparative table.) and he knows and uses all the separate diphthongs and nasals which are used in middle age macedonian ciryllic of the reformer Kliment Ohridski. Especially indicative is the fact that Constantine – Kiril when with his brother Metodi was in Herson, he found a bible and a psalter written “ rousyskimi pismen™” and a man who knew that language, so with him he learnt how to read those books which means that his stay at the Hazars on Crimea enriched Kiril’s knowledge and positively contributed to the formation of the glagolithic, before leaving both the Salonika brothers for Moravia in 863. Doubtless Trp Ruen is not the contemporary of the macedonian reformers and the oak planks are cut-out probably in the year 6.075 from the creation of the world because the sign group
![]()
could have a numerical value of 567, because the same could be deciphered above titled sign group
å . E . D. = 6075 - 5508 = 567 B.C.
This goes to say that the inscription of T’RP RUEN was made two years after the death of UPRAVDA, VISTINIAN, ISTINIAN, or as is better known by his Latin name of JUSTINIAN I - one of the most famous Macedonians (born in the village of Taor, near Skopje,) who ruled with the World Christian Empire (Early Byzantium) during the period 527-565, still known as Emporium Romanum at the time. Vistinian, Istinian or Justinian I is the greatest lawgiver of all time, who conducted codification of the so-called “Roman Law,” and in fact, in the year 528 with a commission of 10 of the best lawyers he ordered that 4,652 previous regulations be collected in one single legal code. Later he also ordered a fifty-volume collection of basic verdicts in which the Ancient Macedonian legal substratum is incorporated as the foundation of the legal system of later European and other legal states.
|
St. Vitale Church, Ravena, mosaic (second quarter of VI century AD) Portrait of Upravda, Vistinian, Istinian or Justinian I (527 - 565 AD) and his 10 best lawyers. |
Heraclea (present
day Bitola,) Great Basilica, nartex, floor mosaic, detail: |
The fact that the colonel of the russian army Theodor Arturovich Izenbek (1890 - 1941) found the original oak planks of the “V LES KNIG” (“V LES KNIG”) by chance in 1919 in Velikiy Burluk – estates of the Zadonian courtiers close to the town Volchanska in the Kurs governory in Russia as part of the nobles home relics in 1922. Ali Izenbek via Constantinopole and France transferred them into Belgium in Brussels and in 1941 probably the special services of the SS (for instance the institute Anerbe) got hold of them and destroyed them as possible traces of the ancient slav culture, absolutely nothing is said about the origins and place of dwelling and working of the author Trp Ruen as a scientist, composer and cutter of the planks of “V LES KNIG” (“V LES KNIG”). However, if we keep in mind that the mountain Ruen is in Macedonian, that the language that Trp Ruen used is closest to the east dialects of the macedonian literary language and if we also bear in mind that Trp Ruen almost completely used the base and the peculiarities of the vocal and consonantal system of the ancient macedonian alphabet then it becomes clear that the author of “V LES KNIG” (“ V LES KNIG”) has his roots in Macedonia that is somewhere in the surroundings of the Ruen mountain and whether the oldest history of the slav people has one author or three authors and how the oak planks “wandered” off and were completed throughout the big wide world is a mater of separate research.
|
Comparative
table with illustration of Ancient Macedonian alphabet, Macedonian
alphabets of the Middle Ages, and modern Macedonian alphabet in
relation to other derivative alphabets of the Macedonian alphabet.
|
|



